Arthosis is a degenerative disease -stric of the joints, characterized by a slow and progressive destruction of the intraarticular cartilage. Arthosis includes a group of joint diseases of an inflammatory destructive nature, which have different causes and similar development mechanisms.
Arthosis is one of the most common diseases in the world that occupies a position of leaders in women and men over the age of 30 and with age the risk of developing the disease increases alone.
The causes of the pathology
Arthosis develops following a violation of the metabolic processes in the joints, in the background of which the intraarticular cartilage begins to lose water and does not become elastic. The predisposing factors of these changes in the cartilage may be internal and external causes:
- hormonal changes;
- Characteristics related to age;
- genetic predisposition;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- Excessive joint load;
- injuries and damage - dislocations, fractures, serious bruises, rupture of ligaments;
- changes in the metabolism within the articulation associated with obesity, diabetes mellitus;
- hypothermia;
- lower and unbalanced nutrition, following which the body does not receive calcium, omega-3 and 6, fat and proteins;
- inflammatory process in the joint;
- violation of the blood flow of the femoral head - perties disease;
- problems with blood coagulation, hereditary diseases;
- Autoimmune diseases - Red lupus, rheumatoid arthritis.
Specific diseases that have nothing to do with the joints, i. e. : i. e. :
- syphilis;
- hyperthyroidism;
- thyroiditis.
At risk are the people who are engaged in a strong physical work, they are forced to constantly hypothermia and experience an increase in the load on musculoskeletal miners, blacksmiths, athletes, removals and pregnant women.
Symptoms of arthrosis
The first symptom of arthrosis is pain at the minimum load of the joint, which passes quickly as soon as the articulation is left alone. Arthosis is characterized by 4 basic clinical signs:
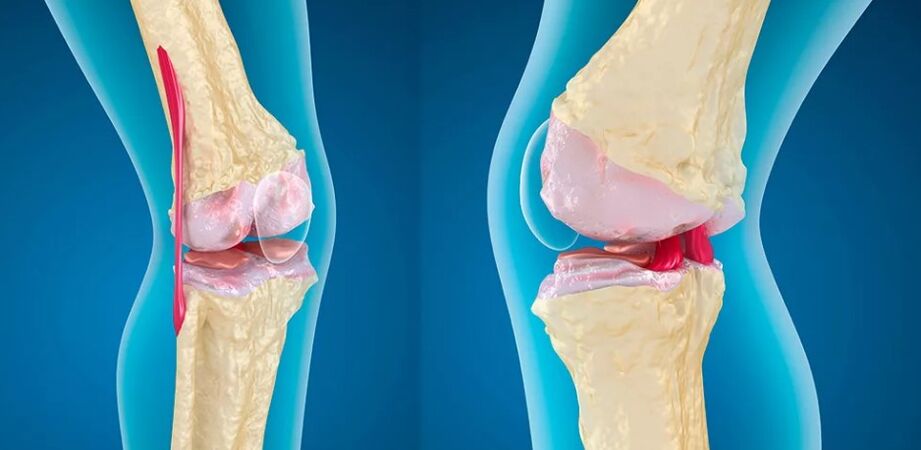
- PAIN - Pain in arthrosis has some characteristics, in contrast with pain in case of random bruises of the articulation or the inflammatory process in it. First of all, you should pay attention to the occurrence of discomfort and pain with any movement and load on the articulation concerned. It is worth stopping moving and removing the load, since the pain passes immediately, that it does not occur when it has injured or inflamed the joint. At night, the articulation collapsed practically does not cause discomfort to the patient, painful sensations are possible only when the position of the body has changed, but pass quickly. With a pronounced progression of destructive processes within the joint, sharp pains can occur at night, which eventually become stronger and make their changes to the lifestyle. Acute pain occurs with any changes over time, the change of the moon phases, the minimum load.
- Crysta - This sound appears to be a decrease in the softness of the rotation of the bones around the joint, which leads to the friction of the bones each other and is accompanied by a characteristic crunch. As the degenerative processes progress in the articulation, the creaking becomes more pronounced and is accompanied by pain.
- Limiting the mobility of the joint - In the initial phase of the development of the pathological process of the pronounced restrictions of mobility, but when the destruction of the joint is underway, it is increasingly difficult for the patient to perform simple actions. In the end, the articulation concerned is completely immobilized.
- Joint deformation - osteophytes begin to actively grow on the bone surface and the synovial fluid accumulates. The deformation of the joint is observed in an advanced degree of pathological process.
The degenerative processes in the joint do not develop rapidly, the disease is characterized by the phases of exacerbation and remission, from which patients are in a hurry to seek medical assistance, thus contributing to the progression of destructive processes within the joint.
Phases
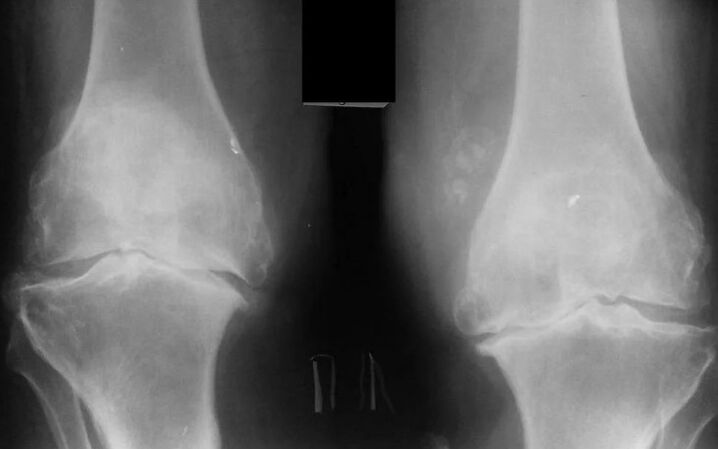
The stage of the progression of the pathological process in the articulation is determined using the X -ray examination. Only 4 phases of the disease are distinguished:
- First - characterized by a slight narrowing of the joint gap, while there are no pathological growths on the bones;
- The second: there is a slight narrowing of the joint gap, osteophytes are formed on the surface of the bone;
- The third: the joint gap is restricted, on the surface of multiple bone osteophytes, the joint is observed;
- The fourth: practically there is no joint gap, there are more osteophytes, a pronounced joint deformation.
Grade
Arthosis is expressed in the form of deductive deductive deductive processes in the articulation, following which the cartilage is influenced, the changes in the capsule and in the synovial joint of the joint are developing, as well as in the ligaments that surround you and in the bone structures. Depending on the seriousness and gravity of these destruction, it is customary to distinguish 3 degrees of arthrosis.
The first degree
There are no pronounced deformations or changes in the joint, but the composition of the synovial fluid is disturbed - this leads to an insufficient supply of joint tissues with nutrients, water and microelements, following which the cartilage becomes quickly not elastic and not adapted to the loads. Over time, this causes inflammatory processes and is accompanied by pain during movement and load on the joint.
At the first degree of arthrosis, none of their patients seek medical assistance, attributing discomfort and pain to an uncomfortable pose during sleep, fatigue and an incorrect lifestyle. Sometimes the patient can see a characteristic creaking in the area of the articulation concerned, but this is not accompanied by severe pain, but only by the discomfort, to which no one pays more attention.
If arthrosis is accidentally diagnosed in the first phase, the disease is easily treated.
The second degree
At this stage, the disease is accompanied by destructive processes of the cartilage tissue inside the joint. Osteophytes grow intensely on the bone surface and the more intensely the load in the area of the damage, the more pronounced the destruction will progress.
At the same time, the patient complains of a constant pain of a real nature, which periodically passes alone and cannot be felt for a long time. So the disease progresses again. Against the background of such a pathological process, the muscles that surround the inflamed articulation gradually lose their functions, from which the patient gets tired quickly and cannot resist physical activity, which has easily endured. In the second degree of arthrosis, the patient gradually progresses the deformation of cartilage and joint.
The third degree
It is the most difficult. The intra -articular cartilage of the affected articulation is more subtle and intensely destroyed, which leads to a clearly evident deformation and the compromised functions of the limb concerned. The ligaments and muscles located next to the joint are lacking in nutrients and oxygen and atrophy gradually, which is accompanied by a pronounced loss of mobility. At the same time, the patient is always tormented by acute pain, which has improved by any attempt to change the position of the body, with changes in weather conditions and in the moon phases and gradually leads to a complete loss of legal capacity.
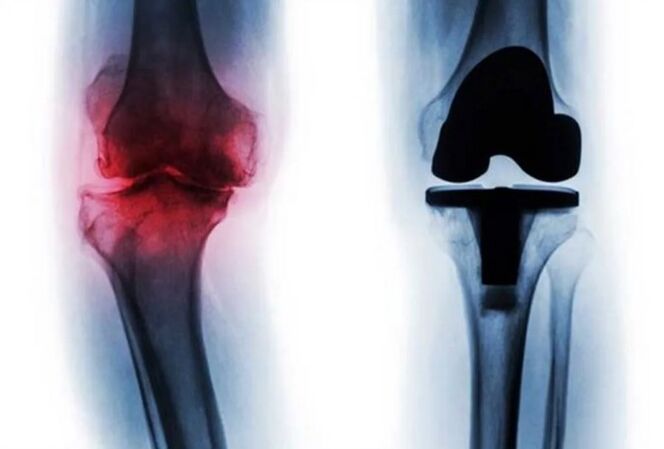
Types of arthrosis
Depending on the cause of the pathological process, primary, secondary and idiopathic arthrosis stands out within the joint.
The primary develops as an independent, secondary disease, following an injury or infection and the cause of the idiopathic form is not known. In addition to the classification of the disease, depending on the cause of the pathological process, arthrosis stands out in the place of location of destructive changes:
- Gonartrosis is the most common type of pathology, characterized by damage to the knee joints. Very often, gonartrosis is detected in people with excess weight, with chronic metabolic diseases in the body, weak immunity. The arthrosis of the knee progresses for a long time and gradually leads to a complete loss of the motor function.
- The osteoarthritis of the ankle - The main causes of the development of degenerative processes in the artery articulation are injuries, disputes, lengthening, fractures. In some cases, the development of the pathological process can cause autoimmune disease - rheumatoid arthritis. The arthrosis of the ankle is subject to dancers, women who wear high heels, athletes.
- The arthrosis of the shoulder joint is the main cause of the degenerative processes in this area are congenital anomalies of the development of the shoulder joint or excessive loads in this area, for example when wearing heavy on the shoulders.
- Coksartrosis or arthrosis of the hip joint - The main cause of the occurrence is the changes related to age in the tissues of the joint. At risk, people over the age of 45.
- The arthrosis of the cervical region: the causes are neck lesions, progressive osteochondrosis, obesity, a sedentary lifestyle. At risk, people who work on the computer are in the offices. In addition to severe neck pain, patients have pronounced dizziness, conscientious inhibition, impairment of memory and fatigue. These symptoms are due to the compression of the vertebral artery through which nutrients and oxygen enter the brain.
- Spondilartrosis - The destructive destruction is subject to fabrics of the spinal column, that is to say its lumbar department. In the risk group of a woman during the occurrence of menopause, since spondularosis progresses against the background of a deficiency of female sex hormones.
- The osteoarthritis of the fingers - develops for the same reason as spondularosis.
- Poliartrosi - characterized by damage to several joints with progressive degenerative processes in them, while ligaments, muscles and surrounding the articulation of the tissue are involved in the pathological process.
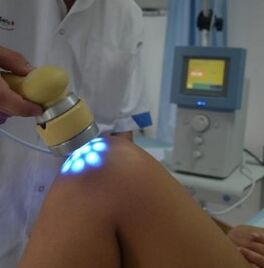
Treatment of osteoarthritis
The treatment of arthrosis is better performed in the early stages, so the disease is better to succumb to the conservative methods of therapy. It is very important to correctly establish the cause of progressive destructive changes in the articulation and stop these factors over time.
The treatment of arthrosis is performed fully and consists in the elimination of the inflammatory process, stopping the pain syndrome, stopping the progression of the pathological process and, if possible, restoring the lost joint functions. Conservative therapy includes the selection of physiotherapy treatment methods and methods.
Pharmacological treatment
The treatment of osteoarthritis is different with different places of location of the pathological process:
- Highths of the fingers and hands -ese anti -anti -inflammatory drugs nonsteric in the form of cream ointments, gel. To prevent the progression of the pathological process, the Condroprotectors technique is shown. After interrupting an acute inflammatory process, massage and physiotherapy methods of therapy are prescribed.
- With the arthrosis of the shoulder joint -inside the joint, the patient is injected with injected pain relievers and non -pounded anti -inflammatory drugs. Oboraly can prescribe intake drugs that relax the muscles and slightly reduce the intensity of pain. After the relief of acute inflammation and pain, physiotherapy and massage are indicated.
- Arthos of the knee joint -Spress anti -anti -inflammatory drugs non -pounds locally in the type of compressive, ointments, gel. The area of the articulation concerned shows physiotherapy methods of therapy.
- The arthrosis of the hip joint: the increased increased ointment or gel of the group group are applied to the lesion area and the pain relievers injected into the joint.
- The arthrosis of the knee joint - Ointments and gels with an analgesic effect are applied to the damage area and after the relief of acute pain and inflammation, physiotherapy treatment methods are indicated.
- HARTROSIS OF THE ARESTH - The patient is recommended by rigorous bed rest with the rest of the affected joint. As the acute inflammatory process attenuates, physiotherapy procedures, bathrooms, massage are prescribed.

Physiotherapy treatment
Effective physiotherapy methods, often used in various degrees of gravity of arthrosis, include:
- The treatment with shock wave effectively eliminates the patient from the outflows of osteophytes, thus eliminating the pain and restrictions of joint mobility;
- Muscle stimulation around the joint affected with electric: this procedure is very effective for patients with pronounced limited mobility and allows you to improve blood circulation in the joint, accelerate regenerative processes, increase muscle tone;
- Ozonotherapy - A mix of gas is introduced into the cavity of the articulation concerned, due to which the patient decreases, the mobility of the joint is normalized and the signs of inflammation disappear. For the maximum effect, ozone therapy is performed in courses;
- FONOFORESI - The effect on the area of damage by ultrasound waves using drugs. This method of using drugs is much more effective, since ultrasound waves provide the drug directly to the lesion.
In addition, the treatment with physi-therapy includes operating therapy, massages, manual therapy, mechanotherapy.
Dietary nutrition
The diet with arthrosis should be the most balanced and rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids, proteins, trace elements. It is recommended to include fresh fish, vegetable oils, cottage, dairy products -Caseari, meat, fresh vegetables and fruit in the diet.
Flour products and "fast" carbohydrates, chocolate, coffee, alcohol, pork, fats and sharp dishes should be excluded from the diet.




















